Appearance
24. 树形与扁平数据结构转换
经典的面试题,首先来分析分析啥是树形和扁平数据结构。
1. 何为树形和扁平数据结构
1.1 扁平化数据结构
扁平化结构的数据如下所示:
js
let array = [
{ id: 1, name: '1', pid: 0 },
{ id: 2, name: '2', pid: 1 },
{ id: 3, name: '3', pid: 1 },
{ id: 4, name: '4', pid: 3 },
{ id: 5, name: '5', pid: 3 }
]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
2
3
4
5
6
7
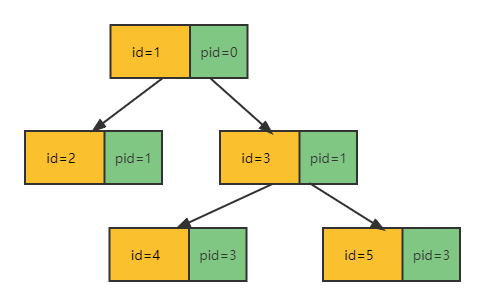
id标识当前节点pid是当前节点的父节点的id
例如节点 { id: 2, name: '2', pid: 1 },它的唯一标识 id 是 2,它的 pid 为 1,意味着它的父节点是 id=1 的节点,也就是第一个节点。
1.2 树形数据结构
分析了以上节点属性与节点关系之后,我们能很快理解下面这个由此转换而来的树形结构 tree:children 里面的就是当前节点的子节点,若无子节点,则为空数组。
js
const tree = [
{
id: 1,
name: '1',
pid: 0,
children: [
{
id: 2,
name: '2',
pid: 1,
children: []
},
{
id: 3,
name: '3',
pid: 1,
// 省略一些属性
children: [{ id: 4, ..., pid: 3 }, {id: 5, ..., pid: 3 } ]
}
]
}
]
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
图示如下:
2. 树形结构 => 扁平结构
树形结构数据转扁平结构,思路和多维数组扁平化类似。
- 从根节点开始,遍历当前节点,把
id、name、pid属性取出,组成新节点newNode加入结果集中; - 然后继续递归查找当前节点取出的
children - 由于使用了尾递归方法,因此继续传入
array
js
const treeToArray = (tree, array = []) => {
for (let node of tree) {
const { children, ...newNode } = node
array.push(newNode)
treeToArray(children, array)
}
return array
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
调用方式:
js
treeToArray(tree)
1
3. 扁平结构 => 树形结构
思路:遍历 array,寻找父节点的所有子节点(根据 node.pid === id 判断,node 是被寻找的子节点),每找到一个就加入到当前父节点中,然后给这个父节点创建新属性 children=[],继续递归查找找每个被加入的新节点 newNode 的子节点。
arrayToTree(array, id, tree) 表示从原来的扁平结构数据中查找 id 节点的所有子节点,并将结果加入到 tree 中。
js
const arrayToTree = (array, id, tree) => {
array.forEach(node => {
if (node.pid === id) {
const newNode = { ...node, children: [] }
tree.push(newNode)
arrayToTree(array, newNode.id, newNode.children)
}
})
return tree
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
调用方式:
js
// 原始数据
// id 标识当前节点,pid 是当前节点的父节点
let array = [
{ id: 1, name: '1', pid: 0 },
{ id: 2, name: '2', pid: 1 },
{ id: 3, name: '3', pid: 1 },
{ id: 4, name: '4', pid: 3 },
{ id: 5, name: '5', pid: 3 }
]
// 初次传入 0,表示从树的根部节点开始生成树结构
arrayToTree(array, 0, [])
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12