Appearance
03. 二叉树遍历模板
以下代码基于此二叉树节点数据结构:
js
function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
this.val = (val === undefined ? 0 : val)
this.left = (left === undefined ? null : left)
this.right = (right === undefined ? null : right)
}
1
2
3
4
5
2
3
4
5
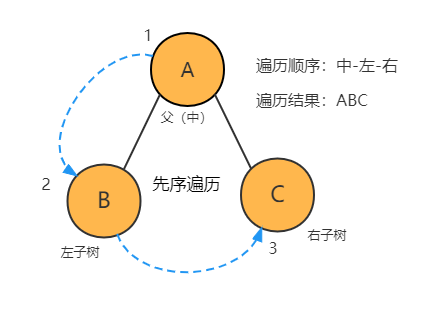
1. 先序遍历
1.1 先序遍历(递归)
先序遍历顺序按照 中(父)-左子树-右子树 的顺序遍历节点。
js
const preOrder = (node, res = []) => {
if (node) {
res.push(node.val) // 中(父节点)
preOrder(node.left, res) // 左子树
preOrder(node.right, res) // 右子树
}
return res
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
1.2 先序遍历(迭代)
js
const preOrder = (node) => {
if (!node) return []
const res = []
const stack = [node]
while (stack.length) {
const n = stack.pop()
res.push(n.val)
n.right && stack.push(n.right) // 右先进,先入后出
n.left && stack.push(n.left) // 左后进,后进先出
}
return res
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
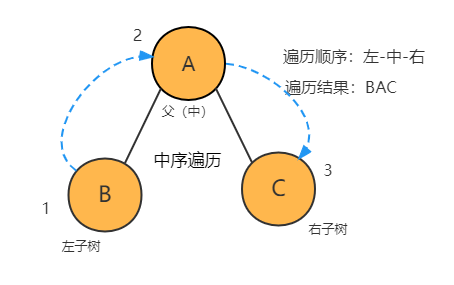
2. 中序遍历
2.1 中序遍历(递归)
中序遍历顺序按照 左子树-中(父)-右子树 的顺序遍历节点。(前序基础上,修改一下访问节点的顺序即可)
js
const inOrder = (node, res = []) => {
if (node) {
inOrder(node.left, res) // 左子树
res.push(node.val) // 中(父节点)
inOrder(node.right, res) // 右子树
}
return res
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2.2 中序遍历(迭代式)
js
function inorderTraversal( root ) {
if (!root) return []
let res = []
let stack = []
let cur = root
while(cur || stack.length) {
while(cur) {
stack.push(cur)
cur = cur.left
}
let node = stack.pop()
res.push(node.val)
cur = node.right
}
return res
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
3. 后序遍历
3.1 后序遍历(递归)
后序遍历顺序按照 左子树-右子树-中(父) 的顺序遍历节点。
js
const inOrder = (node, res = []) => {
if (node) {
inOrder(node.left, res) // 左子树
inOrder(node.right, res) // 右子树
res.push(node.val) // 中(父节点)
}
return res
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
3.2 后序遍历(迭代)
仿照先序遍历,修改为 根右左,因为后序遍历是 左右中,所以反转数组即可。
js
const preOrder = (node) => {
if (!node) return []
const res = []
const stack = [node]
while (stack.length) {
const n = stack.pop()
res.push(n.val)
n.left && stack.push(n.left) // 左后进,后进先出
n.right && stack.push(n.right) // 右先进,先入后出
}
return res.reverse()
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
4. 层序遍历
使用队列实现二叉树的层序遍历,外层 q.length 循环,使用 len 记录外层循环开始时队列 q 中的节点数量,内层循环 len 次,将同层级的节点值保存到同一数组中,同时将下一层的左右子树入队列 q。结合图示阅读代码更好理解。

js
const levelOrder = function (root) {
if (!root) return []
let q = [root], ans = []
while (q.length) {
let len = q.length
let temp = []
while (len--) {
let node = q.shift()
temp.push(node.val) // 每层节点值存入同一个数组
node.left && q.push(node.left)
node.right && q.push(node.right)
}
ans.push(temp) // 同层节点形成的数组存入新数组,形成二维数组
}
return ans
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
层序遍历求树最大深度
层序遍历可以求每一层的节点,也就意味着可以求二叉树的最大深度。
js
function maxDepth( root ) {
if (!root) return 0
let res = 0, queue = [root]
while(queue.length) {
let len = queue.length
while(len--) {
let node = queue.shift()
node.left && queue.push(node.left)
node.right && queue.push(node.right)
}
res++
}
return res
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
也可以使用递归解决:
js
function maxDepth( root ) {
if (!root) return 0
return Math.max(maxDepth(root.left), maxDepth(root.right)) + 1
}
1
2
3
4
2
3
4